Embarking on a journey into the realm of replacement materials, this introduction aims to intrigue and inform readers about the diverse uses and impact of these innovative materials across industries.
Delving into the specifics of each type and application, we uncover the fascinating world of materials that are reshaping the way we build, create, and innovate.
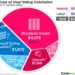
Types of Replacement Materials
Replacing materials in various industries is essential for maintaining efficiency and sustainability. Different types of replacement materials are used to meet specific requirements and challenges. One common option is composite materials, which offer a unique combination of properties and benefits compared to traditional materials.
Let’s explore the different types of replacement materials and their implications.
Composite Materials
Composite materials are engineered materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties. These materials are combined to create a new material with enhanced properties that are not easily achievable with individual components alone.
Some common types of composite materials include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and kevlar.
- Properties and Benefits:
- Composite materials exhibit high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and durability.
- They offer design flexibility, allowing for complex shapes and structures to be formed.
- Composites can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements, such as stiffness, impact resistance, or thermal conductivity.
Natural vs. Synthetic Replacement Materials
When it comes to replacement materials, there is a choice between natural and synthetic options. Natural replacement materials are derived from renewable sources, such as wood, bamboo, or cotton, while synthetic materials are manufactured from chemical compounds. Both types have their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
- Natural Replacement Materials:
- Biodegradable and environmentally friendly.
- May have limitations in terms of strength and durability.
- Renewable source of materials, reducing dependency on finite resources.
- Synthetic Replacement Materials:
- Consistent quality and performance characteristics.
- Often non-biodegradable, contributing to environmental pollution.
- Can be engineered to meet precise specifications and requirements.
Environmental Impact
The choice of replacement materials has a significant impact on the environment. Using sustainable materials can help reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and minimize carbon emissions. It is essential to consider the life cycle of materials, from production to disposal, to assess their overall environmental footprint.
- The use of composite materials can contribute to resource efficiency and waste reduction.
- Opting for natural replacement materials can promote biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Synthetic materials may require more energy-intensive production processes, leading to higher carbon emissions.
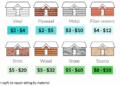
Applications of Replacement Materials
Replacement materials find a wide range of applications across various industries, playing a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and durability in different sectors.
Construction Projects
In the construction industry, replacement materials like recycled concrete, fly ash, and reclaimed wood are commonly used to reduce environmental impact and lower costs. These materials are utilized in foundations, walls, and other structural elements, providing sustainable alternatives to traditional construction materials.
Automotive Engineering
Replacement materials play a vital role in automotive engineering, where advanced composites, carbon fiber, and aluminum alloys are used to reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance overall performance. These materials are integrated into car bodies, chassis, and interior components, contributing to the development of lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles.
Medical Technology
Innovative replacement materials have revolutionized the field of medical technology, with applications in orthopedic implants, dental prosthetics, and tissue engineering. Materials like biocompatible polymers, ceramic implants, and bioactive glasses are utilized to create implants that mimic natural tissues, promote healing, and improve patient outcomes.
These advancements have led to safer and more effective medical procedures, enhancing the quality of patient care.
Manufacturing Processes for Replacement Materials

In the production of replacement materials, various manufacturing processes are utilized to create materials that can serve as alternatives to traditional resources. These processes involve a series of steps that transform raw materials into finished products ready for use in various applications.
Steps in Producing Replacement Materials
- Raw Material Selection: The first step involves carefully selecting the raw materials based on the desired properties of the replacement material.
- Processing: The raw materials undergo processing techniques such as mixing, blending, heating, or cooling to achieve the desired composition and structure.
- Shaping: The processed materials are shaped into the desired form through molding, casting, extrusion, or other shaping methods.
- Curing or Setting: Some replacement materials require curing or setting to attain the necessary strength and durability.
- Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Manufacturing Techniques
- Traditional methods often involve manual labor and rudimentary tools, leading to inconsistencies in the final product. In contrast, modern techniques utilize advanced machinery, automation, and computer-aided design to enhance precision and efficiency.
- Modern manufacturing techniques also focus on sustainability by incorporating eco-friendly practices, reducing waste, and optimizing energy consumption.
- Overall, modern methods offer improved quality, cost-effectiveness, and scalability compared to traditional approaches.
Quality Control Measures in Manufacturing
- Regular inspection of raw materials, intermediate products, and final output to ensure adherence to quality standards.
- Testing of physical, chemical, and mechanical properties to verify the performance and durability of replacement materials.
- Implementation of corrective actions and continuous improvement processes based on feedback and data analysis.
- Certifications and compliance with industry regulations to guarantee the safety and reliability of replacement materials.
Sustainability Practices in Production
- Recycling of waste materials and by-products to minimize environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
- Optimization of resource usage through efficient processes, renewable energy sources, and eco-friendly technologies.
- Reduction of carbon footprint by adopting sustainable practices such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage.
- Collaboration with suppliers, partners, and stakeholders to promote sustainability throughout the supply chain.
Future Trends in Replacement Materials
Advancements in technology continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of replacement materials. From nanotechnology to biodegradable options and the rise of 3D printing, the landscape of materials science is constantly evolving to meet the demands of various industries.
Role of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology has opened up a world of possibilities in the development of innovative replacement materials. By manipulating materials at the nanoscale level, scientists and engineers can enhance the properties of materials, making them stronger, lighter, and more durable. Nanotechnology also allows for the creation of materials with unique properties such as self-healing capabilities, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Biodegradable Replacement Materials
The push towards sustainability and environmental conservation has led to the increased focus on biodegradable replacement materials. These materials are designed to break down naturally over time, reducing the environmental impact of traditional materials that can linger in landfills for centuries.
Biodegradable materials offer a promising solution to reducing pollution and waste, especially in industries such as packaging and construction.
Impact of 3D Printing
D printing technology is revolutionizing the production of customized replacement materials. By layering materials to create complex structures, 3D printing allows for the rapid prototyping and manufacturing of parts tailored to specific requirements. This level of customization not only improves efficiency but also opens up new possibilities for creating materials with unique properties and designs.
Wrap-Up
Wrapping up our exploration of replacement materials, we reflect on the evolution of these materials, the potential they hold for the future, and the exciting possibilities they offer for a more sustainable and advanced world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using composite materials as replacements?
Composite materials offer a combination of strength, durability, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for various applications.
How do replacement materials contribute to sustainability?
Replacement materials often require fewer resources to produce and can be designed to be more eco-friendly, reducing the environmental impact of traditional materials.
What role does nanotechnology play in creating innovative replacement materials?
Nanotechnology allows for the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, leading to the development of advanced and high-performance replacement materials.